Prostate cancer is the most common malignancy in males in the US and Europe: approximately 15.3 % of men will be diagnosed with prostate cancer at some point during their lifetime.1 The majority of patients are diagnosed at an early stage, at which treatments such as radiotherapy or surgery may be curative.2 The first-line treatment for metastatic or advanced prostate cancer is androgen deprivation therapy, which is effective initially, but relapse typically occurs after 18–24 months.3 Progression occurs via androgen receptor signalling, leading to the state of castrate-resistant prostate cancer (CRPC), for which the prognosis is poor.4,5 Current approved therapeutic options for advanced and CRPC include chemotherapy (docetaxel, cabazitaxel), immunotherapy (sipuleucel-T), bone targeted agents (denosumab, radium-223 [RA-223]) and new-generation endocrine therapies (abiraterone acetate, enzalatumide).
Despite major recent advances, metastatic CRPC (mCRPC) remains an incurable disease, although median survival times of up to 33 months have been reported in recent clinical trials6 compared with 1 year of median survival before the 2000s.7 Cross-resistance between hormonal agents has further complicated treatment approaches.8–10 Tumour immunosuppression is a well-established mechanism for the regulation of tumour growth. However, many immunotherapeutic strategies, despite their theoretical promise, have failed to bring about effective, consistent and durable responses in clinical trials of mCRPC. So far, sipuleucel T is the only immunotherapy that was shown to improve overall survival (OS) in mCRPC, though without improvement in progression-free survival (PFS) or quality of life (QoL).11 mCRPC therefore represents a substantial unmet clinical need. A better understanding of the microenvironment of prostate cancer may provide new treatment paradigms.
The microenvironment of a tumour is an essential part of its physiology as it provides a nurturing environment for the malignant process. It was previously thought that cancer cells had the potential to metastasise by releasing factors that modify normal cells into cancer cells. However, according to Paget’s 1889 ‘seed and soil’ hypothesis, ‘bad seed’ (tumours) will only grow in a ‘good soil’ (the tumour microenvironment). This hypothesis has been revisited flowing enhanced understanding of the tumour microenvironment: the mutual interaction between the tumour and its specific microenvironment contributes to tumour formation and metastasis.12Tumour cells often promote the development of an immunosuppressive microenvironment, which favours tumour growth and progression. A greater understanding of the mechanisms by which the immunosuppressed microenvironment interacts with tumour cells may lead to improved diagnostic and therapeutic approaches. This article aims to review our current understanding of the immunosuppressed tumour environment in prostate cancer and its therapeutic targeting.
The Role of the Tumour Microenvironment in Prostate Cancer Development, Progression and Control
In order for a tumour to progress and develop into a life-threatening entity, it must develop certain attributes. These include the ability to move, to degrade tissue matrix, to survive in blood and to being able to establish itself in a new tissue environment. It obtains these attributes via signals from the microenvironment that turn on gene transcription.13 The transformation of proliferating stem cells and subsequent tumour invasion depends on complex interactions between cancer cells and a microenvironment of activated inflammatory cells and stromal cell elements.14 In addition to these components, the tumour microenvironment includes matrix-degrading enzymes, endothelial cells and fibroblasts15 as well as factors that stimulate angiogenesis.16 Fibroblasts are able to buffer the acidity generated in the hypoxic conditions of the microenvironment, allowing more cells to survive the low pH, therefore increasing tumour progression.17
At distal metastatic sites, immune cells and fibroblasts establish premetastatic niches, providing permissive environments for migrating tumour cells to colonise and establish metastasis. Primary and metastatic sites communicate through soluble mediators and exosomes both from primary tumour cells and from immune and stromal cells of the tumour microenvironment.18 In addition, a number of secreted proteins derived from the tumour microenvironment have been found to attenuate the effects of cytotoxic chemotherapy in vivo, promoting subsequent treatment resistance.19,20
In prostate cancer, the unexpected finding that earlier-stage prostate cancer may be more resistant to chemotherapy than CRPC21 has led to the suggestion that prostate cancer passes through a microenvironment dependent state and progresses to a microenvironment-independent state.22 Since chemotherapy predominantly affects tumour cells, this finding suggests that targeting tumour cells is insufficient to prevent prostate cancer progression and that prostate cancer therapies should target the tumour microenvironment. Unlike tumour cells, stromal cells within the tumour microenvironment are genetically stable and therefore represent an attractive therapeutic target with reduced risk of resistance and tumour recurrence.18 Chronic inflammation of the prostate also plays a major role in the development of prostate cancer. Epidemiological studies show that prostate cancer is more common in populations with higher levels of baseline inflammation.23 Inflammatory cytokines promote sustained activation of the transcription factor nuclear factor kappa B (NF-kB), which is correlated with metastatic progression to CRPC.24
Immunosuppressive Components of the Tumour Microenvironment
Inflammation leads to disruption of the immune response and regulation of the tumour microenvironment, although the mechanisms by which specific inflammatory mediators contribute to tumour progression are not fully understood.24 Therefore, recent research has focused on modulation of the immune components of the tumour microenvironment.
As tumours progress, a number of mechanisms are activated that enable them to evade immune surveillance.25,26 Myeloid cells, a heterogeneous population of cells derived from the bone marrow, are actively recruited to the tumour microenvironment.26 Two types of myeloid cells: myeloidderived suppressor cells (MDSCs) and tumour-associated macrophages (TAMs) have been the focus of particular attention.26–29 The levels of MDSCs are greatly enhanced in humans during chronic pathological conditions such as infections, inflammation and cancer. MDSCs are immature myeloid cells that fail to complete their differentiation under chronic conditions typically encountered in the tumour microenvironment and lack the expression of mature myeloid cell surface makers.30 MDSCs inhibit innate and adaptive immunity, promoting tumour immune escape. This is achieved by numerous mechanisms including secretion of cytokines and upregulation of nitric oxide, production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), activation of L-arginase and sequestration of cystine, leading to T cell apoptosis, the nitration of chemokines and T cell receptors, blocking T cell migration and tumour cell killing and ultimately resulting in the inhibition of cytokine production that are crucial for T cell anti-tumour functions.27,29,31–34 MDSCs also impair immune cell function in the tumour microenvironment, an important step in tumour progression. MDSCs inhibit the activation of cells with cytotoxic anti-tumour activity and regulatory natural killer (NK)/NK T (NKT) cells,35,36 as well as modulating the de novo development of regulatory T cells (Tregs) 36
In addition to their immunosuppressive role, MDSCs can also directly stimulate tumour growth and expansion by stimulating pro-angiogenic cytokines and creating a favourable environment for metastasis (see Figure 1).29,30,37 MDSCs are actively recruited to the tumour microenvironment from the bloodstream, a process mediated by chemokines, integrins and adhesion factor molecules, which allows further accumulation of these cells in the tumour microenvironment.28 Hypoxia also stimulates the recruitment of circulating myeloid cells to tissues by promoting expression of genes associated with angiogenesis, metastasis and invasion, which is controlled by transcription factor complexes of hypoxia-inducible factors (HIFs).38
Levels of circulating MDSCs increase with age and are elevated in individuals in remission from cancer. This may be a result of age-related increased levels of inflammatory cytokines that facilitate the formation of MDSCs. Individuals in remission from cancer may continuously produce factors that promote the development of MDSCs.35 This raises a number of questions: do individuals with high levels of MDSCs have a microenvironment that supports tumour growth, and hence have increased risk of developing cancer? Do patients with a history of cancer undergo permanent changes in MDSC production? If so, could this contribute to an increased risk of developing seemingly unrelated cancers or other chronic inflammatory conditions? Larger studies are required to further explore these hypotheses.
The second important cellular components of the tumour microenvironment are TAMs, which have numerous roles in cancer progression (see Figure 2).28,39 In tumour microenvironments, TAMs are polarised towards the M2 phenotype, which affect diverse processes such as suppression of adaptive immunity, promoting angiogenesis, tumour cell proliferation and metastasis during tumour progression.40,41 By contrast, the ‘classically activated’ M1 phenotype promotes immune responses and inhibits angiogenesis, thus suppressing tumour development. The M2 TAMs secrete growth factors and cytokines, causing matrix remodelling, and suppression of the immune system’s ability to alert other immune cells to the presence of cancer cells.42 High levels of TAMs have been associated with poor prognosis in prostate cancer.43 MDSCs and TAMs therefore represent a promising target for therapeutic intervention. Strategies may include inhibition of recruitment to the tumour microenvironment, which may reduce resistance to chemotherapy,44 or partial reprogramming of TAM polarisation towards an M1-like phenotype.
The Role of Secreted and Receptor Proteins in the Immunosuppressed Tumour Microenvironment
In addition to cellular components, other immune components of the tumour microenvironment, including chemokines and cytokines, contribute to tumour growth, progression and host immunosuppression.36,45 Interactions of cancer cells with both cellular and non-cellular components of this microenvironment are mediated via secreted and receptor proteins and specialised proteins that bind to matrix collagen, providing signals for cancer growth and metastasis. Pattern recognition receptors such the receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) and toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4) expressed on tumour cells and myeloid cells in the tumour microenvironment interact with damage-associated molecular pattern (DAMP) molecules in the tumour microenvironment. This interaction leads to sustained activation of intracellular signalling pathways, promoting tumour progression.
RAGE is a membrane-bound or soluble protein that is markedly upregulated by stress and inflammatory mediators in epithelial and myeloid cells, and persistent activation of the receptor underlies many chronic diseases.46 The TLR4 is involved in many chronic inflammatory conditions and also has a major role in signalling in the tumour microenvironment. Its activation by immune cells leads to increased tumour-promoting factors, including nitric oxide synthase (NOS2) and cyclooxygenase-2 (COX2), as well the recruitment of immunosuppressive cell types that reduce host tumour surveillance and diminish therapeutic response.47 TLRs recognise DAMPs, which are nuclear or cytosolic proteins released during cell necrosis. DAMP activation of TLRs initiates signalling cascades, resulting in the release of chemokines and cytokines, pro-angiogenic factors and growth factors, which promote tumour progression. Enhanced TLR expression within the tumour microenvironments has made these molecules attractive therapeutic targets. The role of TLR4 in prostate cancer has not yet been fully established, and further studies are warranted.48
Among the ligands for RAGE and TLR4, DAMP molecules S100A8/A9 and Ca2+-binding proteins with well-known roles in inflammation, have increasingly been recognised as having major roles in tumour growth and metastasis (see Figure 3).49 While S100A8/A9 proteins are powerful apoptotic agents and, in high levels, exhibit anti-tumour properties in vitro, the expression of lower levels in cancer cells has been associated with tumour development, cancer invasion or metastasis.50 They are downregulated during normal differentiation of myeloid precursors in the bone marrow to dendritic cells and macrophages. However, tumourderived factors initiate the upregulation of S100A9. This promotes the generation of MDSCs.49,51 MDSCs express carboxylated glycans, which provide binding sites for S100A8/A9, promoting activation of intracellular signalling pathways and supporting an autocrine feedback that causes further accumulation of MDSCs, which then migrate to tumours.52 S100A8/A9 produced in the tumour microenvironment also interacts with RAGE on tumour cells and promote downstream signalling and expression of protumourigenic genes that lead to subsequent tumour progression.53
In addition to their role in MDSC generation, S100A8/A9 mediate the inflammatory and migratory potential of myeloid cells.54 S100A8/A9 have pro-inflammatory actions, and activate mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signalling pathways and NF-kB,49,55 partly mediated by their interaction with RAGE.56 S100A8/A9 proteins play an important role in metastasis, contributing to the establishment of a pre-metastatic niche comprising immature myeloid cells, MDSCs and endothelial cells, providing a microenvironment that supports the adhesion and invasion of disseminated tumour cells.49,54,55,57 They also recruit inflammatory and tumour cells to metastatic sites.54,58–60
S100A9 is strongly expressed in human prostate cancer epithelial cells,61 and high levels of S100A8/A9 have been associated with time to prostate cancer recurrence.62 Their expression in prostate cancer cell lines is increased by hypoxia and HIF-1.62 Furthermore, the presence of circulating S100A9 has been proposed as a diagnostic marker to distinguish prostate cancer from benign prostate hyperplasia.61
A recent study showed that S100A8/A9 expression in epithelial prostate cancer cells causes enhanced infiltration of immune cells, especially neutrophils, and stimulates settlement of the cancer cells in the lung.63
Both RAGE and TLR4 have been implicated in S100A8/A9 mediated effects in tumour progression. S100A9-TLR4 interaction promotes prostate tumour growth.64 Other RAGE ligands have also been implicated in prostate tumour growth.65 Which receptor is predominant depends on the tumour type, the cell types involved and glycation modifications on the receptor.49 Therefore, inhibiting the function of S100A8/A9 by small molecule inhibitors may provide a novel therapeutic approach to prostate cancer.
Therapeutic Agents Targeting Components of the Tumour Microenvironment
There has been increasing interest in novel therapies that interact with the tumour microenvironment rather than the tumour itself. A number of cancer therapies that target the tumour microenvironment are in current clinical use in other solid tumours. These include the monoclonal antibodies trastuzumab for breast and gastric cancers and rituximab for haematological malignancies; bevacizumab, sunitinib and sorafenib; and agents that inhibit osteoclast function (the bisphosphonate zoledronate and the RANKL inhibitor denosumab).66
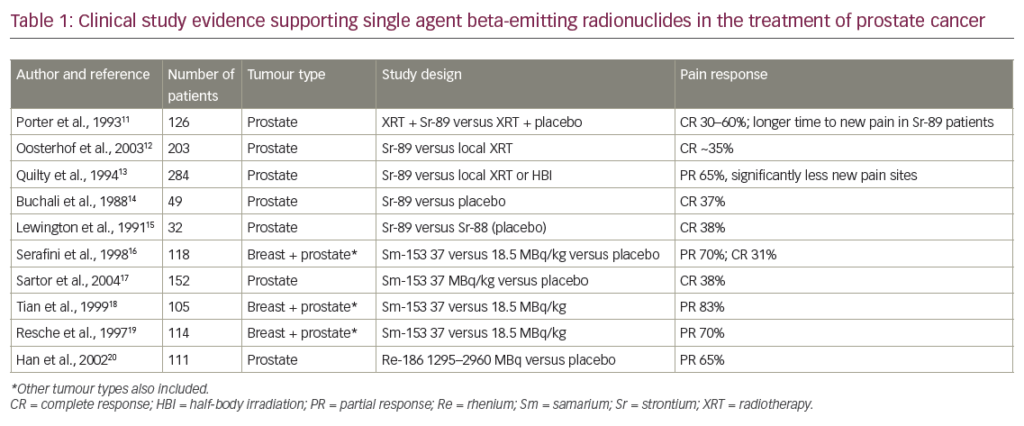
Several microenvironment strategies are in clinical development for prostate cancer and include anti-angiogenesis, integrin signalling and immune pathways. Since prostate cancer is typically a slow-progressing disease, the use of immunotherapy is particularly advantageous in terms of targeting advanced tumours and inducing anti-tumour immunity. Immunotherapies in clinical development include vaccines and antibody-based immunotherapies targeting checkpoint inhibitors.67 Sipuleucel-T is an autologous cellular vaccine consisting of activated antigen-presenting cells loaded with prostatic acid phosphatase. In the pivotal Immunotherapy for Prostate Adenocarcinoma Treatment (IMPACT) phase III study, men treated with sipuleucel-T (n=341) had a median OS of 25.8 months compared with the placebo group (n=171), who had a median OS of 21.7 months, a relative reduction of 22 % in the risk of death compared with the placebo group (hazard ratio [HR] 0.78; 95 % confidence interval [CI] 0.61 to 0.98; p=0.03). However, no difference in PFS was noted. Adverse events (AEs) were more frequently reported in the sipuleucel-T group than in the placebo group, including chills, fever and headache.11 Based on these results, in 2010 sipuleucel-T received approval from the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA), the first therapeutic vaccine approved for any type of cancer in the US.
Ipilimumab is a fully human, monoclonal antibody (mAb) against cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen 4 (CTLA-4), which regulates T cell responses and downregulates the immune response to tumour cells.68 Two phase III trials in the first- and second-line treatment of mCRPC have recently completed accrual.69,70 Results of one of these studies were recently reported. Men were randomised to bone-directed radiotherapy before either ipilimumab (n=399) or placebo (n=400).70 Median OS with ipilimumab was not significantly improved compared with that with placebo (11.2 versus 10 months, HR=0.85, 95 % CI 0.72–1.00; p=0.053). Treatment-related AEs were common and mainly immune-related. Patients without visceral metastases seemed to benefit more, emphasising the importance of optimal patient selection in trials evaluating vaccines and other immunotherapeutic agents for CRPC.
Tasquinimod is an orally administered derivative of quinoline-3- carboxamide that targets the tumour microenvironment and inhibits the growth and metastasis of tumour cells by inhibiting angiogenesis and by enhancing the immune response (see Figure 4).71–73 In addition, it appears to modulate the accumulation and function of regulatory myeloid cells and promotes local tumour immunity by blocking the interaction between the S100A9 and pro-inflammatory receptors such as RAGE and TLR4.74 Tasquinimod has shown anti-tumour effects in several tumour models: including increasing the number of tumour infiltrating CD8+ T cells71 and reducing the accumulation of MDSC populations.75 Tasquinimod also has anti-angiogenic effects in prostate tumours, which may be mediated through histone acetylation of regulatory genes.76 It also increases tumour levels of thrombospondin-1 (TSP1), an endogenous anti-angiogenic agent that promotes the recruitment of M1 phenotype TAMs.77
In a phase II study of 206 men with minimally symptomatic mCRPC, tasquinimod significantly slowed progression and increased PFS: 69 % of tasquinimod-treated patients were progression free at 6 months compared with 37 % of the placebo group (p<0.001) and median PFS was increased from 3.3 to 7.6 months (p=0.0042) (see Figure 5).78 All AEs were in general, transient and manageable. Long-term follow-up data showed that OS after tasquinimod treatment was longer than previously reported in this patient group.79 A phase III clinical trial of patients with mCRPC is ongoing in a similar patient population. The primary endpoint is radiological PFS and the trial is powered to show an effect on OS.80 A phase II trial is also investigating the use of tasquinimod as maintenance therapy in mCRPC after chemotherapy with docetaxel.81 In addition, tasquinimod has demonstrated promise in preclinical studies when administered prior or subsequent to androgen deprivation therapy.82
Combination therapies targeting multiple tumour pathways represent an appealing strategy but confer the risk of additional toxicities. Since the inhibitory effects of MDSCs on innate anti-tumour immunity have presented a barrier to immunological approaches to prostate cancer, there is a strong rationale for combining tasquinimod with immunotherapy.83 Preclinical studies have demonstrated that tasquinimod in combination with tumour-targeted superantigens (TTS, an immunotherapy) confers enhanced anti-tumour effects.75 Tasquinimod may also be employed in combination with chemotherapy82 and radiation, though clinical data are missing at the moment.84 MDSCs have also been implicated as a mechanism of tumour resistance to anti-angiogenic therapies, providing a foundation for future research into combinations of tasquinimod with these agents.85
Other Potential for Targets for Therapeutic Intervention
Pro-angiogenesis Factors in the Tumour Microenvironment
Angiogenesis is essential for the development of tumours; without the development of new blood vessels, tumours are only able to grow to 1–2 mm3. As the tumour outgrows its blood supply, the tumour microenvironment becomes hypoxic86 and the HIF pathway is activated, mediated by the transcriptional regulators HIF-1a and HIF- 2a. This pathway facilitates tumour neovascularisation.62 Signals within in the tumour microenvironment stimulate myeloid cells to promote angiogenesis. Furthermore, certain populations of myeloid cells inhibit the response of tumours to anti-angiogenic agents.87 Inhibition of tumour angiogenesis through inhibition of the vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) signalling pathway, therefore provides a promising therapeutic target. However, clinical trials investigating bevacizumab,88,89 sunitinib,90 sorafenib91 and imatinib92 have demonstrated limited efficacy and significant toxicities.
Integrins
In addition to the accumulation of macrophages and fibroblasts, the tumour microenvironment also includes a group of cell surface receptors called integrins, which are involved in activation and expression of proteases that aid in extracellular matrix (ECM) degradation, in the cell–cell adhesions that must be broken for migration to occur, as well as transferring information between cells and the ECM.93 Integrins, in particular the avß3- and a5ß1-integrins, also play an important role in angiogenesis. The manipulation of integrin signalling may provide a target for therapeutic intervention. Antibodies targeting integrin are in clinical development for prostate cancer.94 Cilengitide has, to date, demonstrated only modest clinical efficacy in mCRPC.95
The Bone Microenvironment
The bone microenvironment is an important therapeutic target in mCRPC since it is estimated that 90 % of prostate cancer patients experience bone metastases.96 Numerous molecular events in the bone microenvironment are involved in bone metastasis in mCRPC.97 Recent research indicates that stromal elements of the bone microenvironment mediate the development of bone metastasis in mCRPC.22,98 Denosumab is a fully human mAb that inhibits normal and tumour-associated bone lysis by preventing RANKL-mediated formation and activation of multinucleated osteoclasts or giant cells from RANK-positive mononuclear preosteoclasts and macrophages, with demonstrated impact on ongoing osteolysis in randomised phase II trials.99,100
In a phase III trial conducted in 1,904 patients with bone metastases from CRPC, denosumab was compared with zoledronic acid. Median time to first on-study skeletal-related event (SRE) was 20.7 months (95 % CI 18.8–24.9) with denosumab compared with 17.1 months (15.0–19.4) with zoledronic acid (HR 0.82, 95 % CI 0.71–0.95; p=0.008 for superiority).101 In a second randomised phase III trial, denosumab also significantly prevented the onset of bone metastases in patients with CRPC though the benefit was moderate and mostly considered non-clinically relevant, except perhaps for specific high-risk subgroups102 (median metastasisfree survival: 29.5 [95 % CI 25.4–33.3] versus 25.2 [22.2–29.5] months; HR 0.85, 95 % CI 0.73–0.98; p=0.028).103
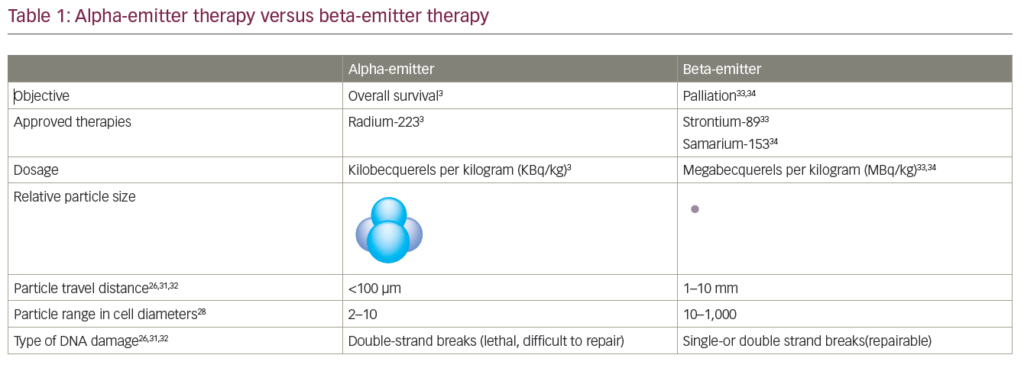
Radium-223 chloride (Ra-223) is an alpha-emitting radioisotope that targets osteoblastic metastasis. In a recently reported randomised phase III trial in men with symptomatic bone-metastatic CRPC who had received or were ineligible for docetaxel chemotherapy, 922 patients were randomised to Ra-223 (n=615) or placebo (n=307). In a planned interim analysis (n=809), Ra-223 significantly improved OS (median 14.0 months versus 11.2 months placebo; p=0.00185; HR=0.695; 95 % CI 0.552–0.875). A rate of SREs was lower in the Ra-223 group, and the time to the first SRE was significantly delayed (median time to SRE 13.6 months versus 8.4 months, respectively; p=0.00046; HR=0.610; 95 % CI 0.461–0.807).104,105 The treatment also demonstrated a favourable safety profile and, as a result, the FDA and European Medicines Agency (EMA) approved Ra-223 for the treatment of mCRPC that has metastasised to bones in 2013.
In a phase II trial, the tyrosine kinase inhibitor cabozantinib caused bone metastases to partially or completely resolve in 85 % of patients with CRPC.106,107 Studies are now exploring the relationship the bone microenvironment and prostate cancer in epithelial tissue and the ability of the cancer to migrate from its origin in the prostate.108
Summary and Concluding Remarks
Treatment approaches successfully employed in many cancers have not proved successful in the management of mCRPC, suggesting that new paradigms are required. The main role of the tumour microenvironment in the development and progression of prostate cancer provides novel targets for therapeutic intervention. Many cellular and molecular components of the immunosuppressed tumour microenvironment have been identified as potential therapeutic targets, including MDSCs, TAMs and the pro-inflammatory protein S100A9. Immunotherapies such as sipuleucel-T and ipilimumab are novel therapeutic strategies with great potential in mCRPC.109 Tasquinimod has demonstrated an ability to modulate the tumour microenvironment in preclinical models, and clinical studies to date have demonstrated promising efficacy and safety in patients with prostate cancer. In addition, preclinical studies indicate that it may enhance the effect of other therapies such as androgen deprivation therapy and chemotherapy. Further preclinical and clinical testing will fully exploit its therapeutic potential as a novel agent targeting the tumour microenvironment rather than direct action on tumour cells. The bone microenvironment is also a promising therapeutic target, with denosumab and Ra-223 proving promising treatment options. Further investigation of components of the tumour environment should help expand the treatment armamentarium for mCRPC.