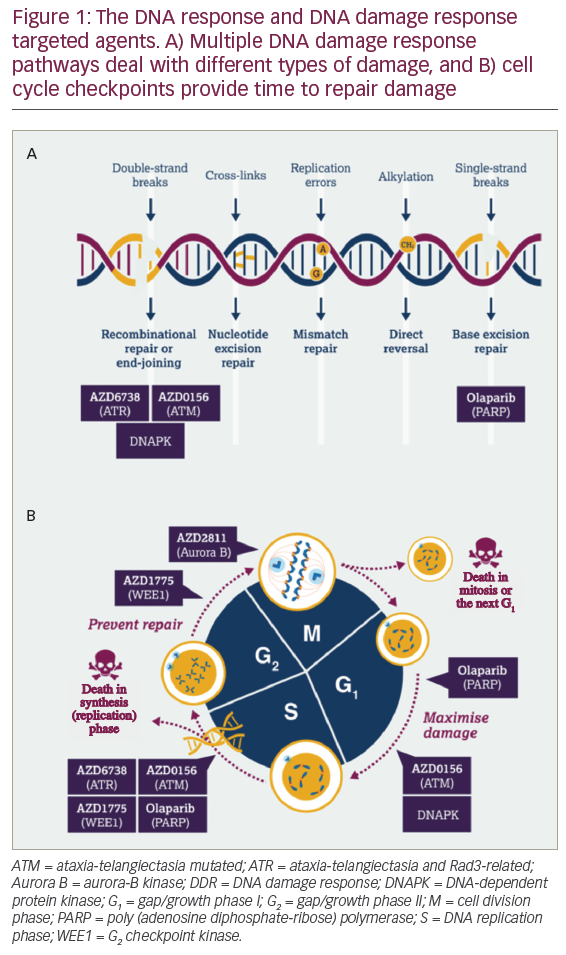
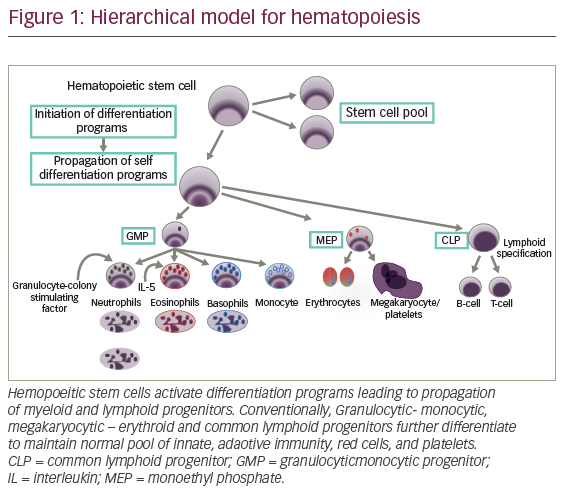
In the originally published article there was an error in the abbreviations for Figure 1. The abbreviation “MEP” was incorrectly defined as “monoethyl phospohate”; this should read “megakaryocytic erythroid progenitor”.
My Learning
Login
Sign Up FREE
Register Register
Login
Trending Topic

12 mins
Trending Topic
Developed by Touch
Mark CompleteCompleted
BookmarkBookmarked
Allan A Lima Pereira, Gabriel Lenz, Tiago Biachi de Castria
NEW
Despite being considered a rare type of malignancy, constituting only 3% of all gastrointestinal cancers, the incidence of biliary tract cancers (BTCs) has been increasing worldwide in recent years, with about 20,000 new cases annually only in the USA.1–3 These cancers arise from the biliary epithelium of the small ducts in the periphery of the liver […]
touchREVIEWS in Oncology & Haematology. 2025;21(1):Online ahead of journal publication