Mutations of the β-globin gene (HBB) cause sickle cell disease and β-thalassaemia, collectively named the β-haemoglobinopathies. As mankind’s most common severe genetic diseases, where they are most prevalent, public health systems can be stressed.1–3 123Asymptomatic heterozygous carriers are protected from severe P. falciparum infection. This has allowed the causative genes to reach polymorphic frequencies in some tropical and subtropical parts of the world.4,5 45Treating the far less prevalent but seriously ill patients with homozygotic mutations is difficult and costly.
The pathophysiology of sickle cell disease is initiated by deoxy-sickle haemoglobin (HbS; α2βS2) polymerization. Insufficient β-globin synthesis in β-thalassaemia results in excessive toxic free α-globin leading to ineffective erythropoiesis, causing severe anaemia. Foetal haemoglobin (HbF; α2γ2) prevents HbS polymerization. In β-thalassaemia, HbF compensates for the deficit of normal haemoglobin (HbA; α2β2). With 30% HbF in the sickle erythrocyte, complications of sickle cell disease nearly disappear. Sufficient HbF In β-thalassaemia erythrocytes ameliorates ineffective erythropoiesis and haemolysis.1–3123
A single mutation in the first exon of HBB (β7 GAG>GTG) causes sickle cell disease. This transversion replaces glutamic acid with valine. When paired with an α-globin chain, the sickle β-globin chain (βE7V) forms HbS. The proximate cause of pathophysiology in sickle cell disease is the polymerization of HbS. The HbS polymer injures the sickle erythrocyte leading to vaso-occlusion and haemolysis. Homozygosity or compound heterozygosity for β-thalassaemia mutations, and sometimes compound heterozygosity for a thalassaemia mutation and a variant haemoglobin such as HbE, causes a β-thalassaemia phenotype. HbS is a haemoglobin variant; in β-thalassaemia the primary amino acid sequence of β-globin is almost always normal. β-thalassaemia mutations result in either insufficient (β+) or a total absence (β0) of β-globin gene expression. With this deficit in β-globin, excess α-globin becomes unstable, leading to erythroblast injury causing ineffective erythropoiesis, haemolytic anaemia and increased iron absorption.
Curing inherited diseases by somatic cell gene therapy was aspirational but now approaches reality.6,7 67It had been hypothesized that the failure of a newborn’s erythrocytes in sickle cell anaemia to sickle as readily as their mother’s cells – even though the mother had sickle cell trait – as well as the paucity of symptoms in newborns with sickle cell anaemia, were attributable to the high HbF levels in infancy. 8 Expand ReferenceLaboratory and clinical investigation suggested that if about one-third of the haemoglobin within a HbS-containing erythrocyte was HbF, this cell would be fully protected from polymer-induced damage. If nearly all erythrocytes contained sufficient HbF there would be few, if any, manifestations of sickle cell disease or β-thalassaemia. The phenotype of compound heterozygotes for HbS and gene deletion types of hereditary persistence of HbF (HPFH) validates the ability of high levels of HbF in erythrocytes with high concentrations of HbS to prevent the phenotype of sickle cell disease. These individuals have about 30 % HbF in most of their erythrocytes, with the remainder being HbS. Clinically they are usually well without presenting with anaemia. 9,10 910Understanding how HbF inhibited polymerization of HbS, knowing the residues in HbF responsible for this inhibition, finding how to best harvest, culture, genetically manipulate and transplant haematopoietic stem and progenitor cells (HSPCs), along with the development of programmable nucleases have led to the clinical approval of gene therapy for transfusion dependent β-thalassaemia and sickle cell disease.11,121112
In this manuscript, clinical gene therapy approaches to treat sickle cell disease and transfusion-dependent β-thalassaemia are described. HSPCs are obtained from patients with these diseases, corrected either by gene addition or genomic editing, and returned to the patient. Short-term results obtained showed disappearance of symptoms in patients with sickle cell disease and transfusion independence in patients with β-thalassaemia. Long-term efficacy and safety require additional follow up.
Inducing foetal haemoglobin
Haemoglobin gene expression switches during progression from embryo to foetus to adult. The switch starts midway through gestation as HbF production falls and HbA production increases. It is normally complete within months after birth. In normal adults, HbF constitutes <1% of total haemoglobin. Depending on the haplotype of the HbS gene, adults with sickle cell disease have between 5% and 16% HbF; homozygotes for β0-thalassaemia have 100% HbF, albeit at concentrations insufficient to sustain normal life. 13 Expand ReferenceThe controls of the switching process are partly understood. Switching is most dependent on the activation of HbF repressors like the genes BCL11A and ZBTB7A.13–15131415
Cell-based therapies inducing about 40% HbF, or a HbF-like haemoglobin in most erythrocytes, can – at least for the duration of the studies to date – ‘cure’, or ‘nearly cure’, β-haemoglobinopathies. In sickle cell anaemia, HbF exerts its powerful effect because it dilutes the concentration of HbS; more importantly, the chances of both the HbF tetramer and the hybrid tetramer α2γβS entering the HbS polymer phase are nil.16 Expand ReferenceIn β-thalassaemia, γ-globin pairs with α-globin, forming HbF.
Erythrocytes with HbF detectable by fluorescent activated cell sorting (FACS) are called F-cells. They arise randomly from erythroblasts that give rise to both HbF-containing and non-HbF containing erythrocytes. F-cells are not foetal erythrocytes even though they have high levels of HbF.17 Expand ReferenceF-cells survive longer than non-HbF cells; in sickle cell anaemia 2–80% of red cells are F-cells. Hydroxyurea treatment increases the number of F-cells and the concentration of HbF/F-cell.
Normal erythrocytes contain ~30 pg of haemoglobin. The threshold for F-cell detection by FACS is 4–6 pg of HbF/F-cell. When HbF/F-cell is 9–12 pg, deoxyHbS polymerization should be prevented at physiologic venous and capillary O2 saturations of 40–70%, affording the sickle erythrocyte nearly total protection from HbS polymer-induced damage. In HbS-HPFH where the total HbF level is ~30%, each cell has ~10 pg of HbF. These cells do not contain HbS polymer. Patients with sickle cell anaemia treated with hydroxyurea or patients with HbS-δβ-thalassaemia can have total HbF levels similar to those in HbS-HPFH, but are usually anaemic and symptomatic. The contrast between these conditions results from the pancellular distribution of HbF in HbS-HPFH versus its heterocellular distribution in the other disorders. Measuring HbF level or F-cells cannot predict disease complications in an individual because neither measure accounts for the variable distribution of HbF levels amongst F-cells. Modelling possible distributions of HbF/F-cell in patients with HbF levels of 5%, 10%, 20% and 30% showed that it is nearly impossible to have a clinically important number of fully protected F-cells when HbF is 5%; no more than 15% of cells can be protected when HbF is 10%. Most patients with these HbF levels have many complications. When HbF levels reach 20%, it is possible for nearly 25% of F-cells to have polymer-inhibiting HbF levels. HbF near 30% can be associated with relatively mild phenotype due to the possibility of up to 70% of cells being protected. The number of F-cells with polymer-inhibiting concentrations of HbF is likely to be a more important determinant of the features of sickle cell anaemia than the total number of F-cells or the concentration of HbF in the haemolysate (Figure 1).18Expand Reference
Figure 1: Heterocellularity of HbF expression: All HbF levels are not therapeutically equal
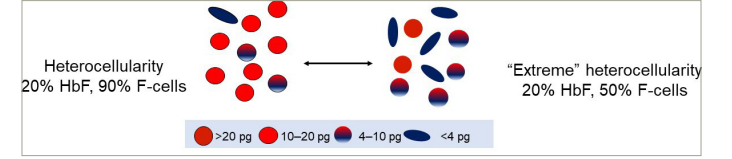
An example of HbF distribution in two individuals with HbF of 20%. On the left, 90% of cells are F-cells. Most have HbF between 10–20 pg. On the right is an example of ‘extreme’ heterocellularity, with 50% being F-cells and some containing HbF levels of >20 pg.
HbF = foetal haemoglobin.
The HbF response in gene therapy differs from the HbF response to hydroxyurea. HbF levels above 20% are uncommon in adults treated with hydroxyurea. Macrocytosis with increased mean corpuscular haemoglobin (MCH) levels accompanies the HbF response. This permits greater heterogeneity of HbF among F-cells so that some F-cells can have very high HbF concentrations while more cells can have HbF concentrations below those needed for full protection. Macrocytosis, where mean corpuscular volume (MCV) increases from about 80 fL to about 90 fL is a feature of hydroxyurea treatment for children with sickle cell disease who have mean total haemoglobin levels of 9.5 g/dL and HbF of 31.5%.19Expand Reference Macrocytosis is mild during HbF induction by gene therapy where pre- and post-treatment MCH levels have been similar. For example, following genomic editing of BCL11A, when HbF level was 44.4%, MCH and MCHC were 29.8 pg and 34.4 pg, respectively, compared with baseline levels of 29.1 pg and 34.1 pg. 20 Expand ReferenceGene therapy increased both F-cell number and HbF/F-cell; hydroxyurea increased F-cell numbers, but not γ-globin gene transcripts/F-cell. 21 Expand ReferenceAs HbF increased to 40% without a major increase in MCH, the near-pancellular expression of HbF at anti-sickling haemoglobin concentrations was inevitable given the observed haematologic constraints resulting in the correction of the sickle cell disease phenotype. 22 Expand ReferenceBecause HbF concentration/F-cell is not uniform, gene therapy-treated patients might have small populations of sickle erythrocytes with low HbF levels, which could account for the persistent low-grade haemolysis sometimes observed.
Clinical trials targeting HbF repressors by genomic editing
The genome editing repertoire is rapidly expanding. Gene editing using CRISPR-Cas9 dominates the field because of the ease of using guide RNAs directing the CRISPR complex to specific DNA sequences. Most sites in the genome can now be reached. 23,24 2324Following double-strand DNA breaks, non-homologous end joining repair disrupts the normal sequence in the targeted area introducing small insertions or deletions. CRISPR-Cas9 can be targeted to disrupt specific erythroid enhancer motifs or binding sites for HbF repressor proteins, thus derepressing HbF production. In addition to the ability to create small deletions and insertions using ‘traditional’ CRISPR-Cas9 technology, it is also possible to achieve some single base edits by ‘nicking’ but not cleaving DNA.
In the first report of gene editing with CRISPR-Cas9 using a guide RNA specific for the erythroid enhancer region of BCL11A, a single infusion of autologous edited CD34+ cells (exa-cel) were given to patients with sickle cell anaemia and β-thalassaemia. Engraftment occurred after 30 days. In the patient with sickle cell disease with baseline HbF of 9.1%, HbF levels increased to 25.9% after 2 months and appeared to stabilize between 46–48% after 1 year. F-cells increased from 33.9% to 99.7%, total haemoglobin stabilized at 11– 12 g/dL, and vaso-occlusive episodes stopped. The patient with transfusion-dependent β-thalassaemia, treated similarly, achieved HbF of >97% of the haemolysate with a haemoglobin concentration of 14 g/dL at 15 months. 20 Expand ReferenceThese early results were extended into pivotal phase III trials of ex vivo editing of mobilized autologous CD34+ HSPCs from patients with sickle cell disease (CLIMB SCD-121; ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT03745287) and transfusion dependent β-thalassaemia (CLIMB THAL-111; ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT03655678).25,262526 Patients were aged between 12 and 35 years. Patients with sickle cell disease had at least two episodes of acute pain in each of the 2 years prior to screening, while patients with thalassaemia with β0/β0 genotypes had a history of ≥100 mL/kg/year or ≥10 units/year of packed red blood cell transfusions in the previous 2 years. Prespecified interim analyses evaluated efficacy and safety in two groups: a full analysis set of participants who received exa-cel infusion, and a primary efficacy set of participants followed for ≥16 months after exa-cel infusion (evaluable for primary and secondary endpoints). This interim analysis was carried out once the primary efficacy set included 27 participants in CLIMB THAL-111 trial and 17 participants in CLIMB SCD-121 trial. Study endpoints are shown in Table 1.
Table 1: Endpoints of CLIMB THAL-111 trial for transfusion-dependent β-thalassaemia and CLIMB SCD-121 trial for sickle cell disease27Expand Reference
|
|
Transfusion-dependent β-thalassaemia |
Sickle cell disease |
|
Primary efficacy endpoint |
Proportion of patients who are transfusion-independent for 12 consecutive months with average haemoglobin of ≥9 g/dL (TI12) |
Proportion of participants free of severe VOCs for ≥12 consecutive months (VF12) |
|
Key secondary endpoint |
Proportion of patients who are transfusion-independent for 6 consecutive months with average haemoglobin of ≥9 g/dL (TI6) |
Proportion of participants free from in-patient hospitalization for severe VOCs for ≥12 consecutive months (HF12) |
|
Secondary & other efficacy endpoints |
|
|
|
Safety endpoints |
|
|
CD34 = cluster of differentiation 34;HbF = foetal haemoglobin;VOC = vaso-occlusive crisis.
Both trials met the primary and key secondary endpoints. In thalassaemia, transfusion independence continued for up to 40.7 months; in sickle cell disease, episodes of acute pain disappeared, with no hospitalizations for sickle cell acute events recorded for up to 36.5 months. In previously transfusion-dependent β0-thalassaemia, 24 of 27 participants met the primary (TI12) and key secondary (TI6) endpoints (p<0.0001), with normal mean haemoglobin and a mean transfusion-free duration of 20.5 months. Three participants who did not meet the primary and key secondary endpoints have either stopped transfusions or had 80% and 96% reduction in transfusions. In sickle cell disease, 16 of 17 participants (94.1%) met the primary endpoint (VF12) of being acute event-free for at least 12 months (p=0.0001), with a mean acute event-free duration of 18.7 months. All 17 participants met the key secondary endpoint (HF12) of no in-patient hospitalizations for acute events for at least 12 months (p<0.0001). In addition, all participants had early and sustained increases in total haemoglobin and HbF that was distributed nearly pancellularly. Markers of haemolysis normalized or decreased. Patient-reported quality-of-life measures improved by month 6 and were sustained through month 24. Stable high-level BCL11A editing was seen in bone marrow and peripheral blood: 84.4% and 74.4%, respectively, at 6 months, and 87.6% and 77.3%, respectively, at 24 months, suggesting that a long-lived HPSC was successfully modified and the effects of treatment should be durable. The safety profile of exa-cel was consistent with busulfan myeloablative conditioning and autologous haematopoietic stem cell transplantation based on the 83 participants who were dosed.27Expand Reference Available evidence, albeit limited, strongly suggests that induction of HbF to levels >40% in sickle cell disease will not adversely impact foetal development or normal physiology. In β0-thalassaemia homozygotes, the high oxygen affinity (low P50) associated with 100% HbF may hypothetically cause babies to have a lower birth weight than normal, a far better outcome than the fraught pregnancies in transfusion-dependent β-thalassaemia.28Expand Reference
In another gene therapeutic approach, engineered CD34+ cells were transduced with a lentiviral vector containing a ‘foetal-like’ HbA gene (HbAT87Q) in 35 patients with sickle cell disease with at least four acute painful episodes in the 2 years before enrollment. In 25 patients evaluated after 6 months, acute events stopped, haemoglobin increased to about 11 g/dL and 40% of total haemoglobin was HbAT87Q, detectable in 85% of erythrocytes. Haemolysis was not eliminated, but was mild.29Expand Reference Similarly encouraging results with the same vector were found in 23 patients with non-β0/β0, a genotype intrinsically milder than the homozygous β0 genotype, where 91% of 20 evaluable patients had sustained average haemoglobin levels of 11.7 g/dL over 29.5 months (ClinicalTrials.gov identifier: NCT02906202).30Expand Reference The same treatment used in 9 patients with either β0/β0 or severe β+ genotypes decreased transfusions by 73%, eliminating them in 3 patients.31Expand Reference
Knocking down BCL11A mRNA using an inhibitory microRNA delivered through lentiviral transduction of CD34+ cells, led to a 90% reduction of BCL11A mRNA with 60–70% γ-chain and HbF expression. In 6 patients with sickle cell disease followed for 7 to 29 months, HbF was 20.4–41.3%, levels of F-cells were 58.9–93.6%, haemoglobin levels were 9.3– 11.4 g/dL and HbF/F-cell was calculated to be 9.0– 18.6 pg; patients had few or no symptoms.32Expand Reference
Disrupting the HbF gene promoters with CRISPR-Cas9 in 3 patients with sickle cell anaemia resulted in HbF levels of 22–29%, F-cell levels of 69.7–87.9% and continued mild haemolytic anaemia, with a reduction, but not cessation, of acute sickle vaso-occlusive events. These results, while short term in only 3 patients, seem inferior to those of the other three reported gene therapy trials, illustrating the importance of achieving HbF levels high enough to force ‘curative’ levels of pancelluarity.22,332233
Conclusion
Beyond these phase II/III clinical trials, the field is rapidly being transformed by in vivo delivery of base or prime editors via lipid nanoparticles or viral vectors directed to HPSCs, which target HbF repressor protein binding domains or the site of the HbS mutation.34–3734353637 Ultimately, if cell-based or vectorized genetic modalities are safe, effective and similarly priced, how might one choose between them and allogeneic stem cell transplantation? Gene therapy does not require the immunosuppression associated with allogeneic stem cell transplantation. Off-target consequences of genome editing, adverse effects of semi-random integration of lentivirus and the sustainability of therapeutic effects need long-term investigation. Experience with allogeneic transplantation is far greater and matched-sibling transplants, especially in young children, provide excellent results.38Expand Reference Gene therapy will also have to compete with the improving prospects for haploidentical allogeneic transplantation. Myeloablative genotoxic conditioning is currently the standard for all cell-based therapeutics. For enhanced safety and greater acceptance, other forms of conditioning are being developed.33,393339 Approved and soon to be approved gene therapies for β-haemoglobinopathies are likely to be the first steps in a long process leading to an effective ‘curative’ treatment for mankind’s most common monogenic diseases.